In aluminum extrusion plants, surface scratches, black spots, adhesion, and inconsistent extrusion speeds are common production defects.
Many engineers believe these problems stem from the setup of the extrusion die or extrusion press, but in reality, one of the most significant factors lies at the contact point between the profile and the conveying material.
For decades, graphite sheets have been the material of choice for extrusion outlets and cooling stations, but as the requirements of extrusion production lines continue to increase, heat-resistant felt is cleaner, safer, and more surface-friendly than graphite.
Read this article to understand why High-temperature felt has become a superior solution for modern aluminum extrusion production lines.
Graphite sheets are essential materials for copper, zinc, and aluminum extrusion presses. These flat, durable sheets are made from natural or synthetic graphite. Graphite sheets are a high-temperature composite material, produced by mixing 99.5% pure flake graphite with thermosetting resin and carbonizing at 1200–1500°C.
Some high-end graphite sheets are coated with boron nitride to improve lubricity and thermal stability.
Their characteristics include: self-lubricating structure with a coefficient of friction of approximately 0.1–0.2; high thermal stability, capable of operating below 600°C under extrusion conditions; and good dimensional stability, maintaining structural stability even under heavy mechanical loads.
Graphite sheets are commonly used in discharge tables, die exits, and some load-bearing locations.
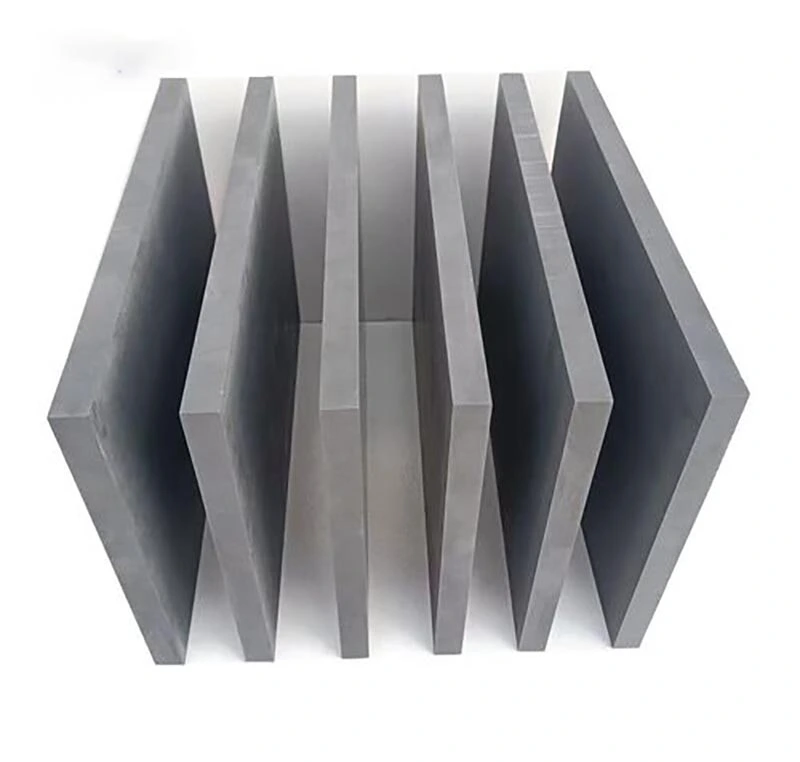
Heat-resistant felt is made from a blend of various high-temperature resistant fibers (such as Kevlar fibers) through processes such as carding, blending, and needle punching, forming a dense and elastic material.
Depending on the extrusion temperature and application, manufacturers typically choose from: PBO felt (maximum temperature resistance 600°C), Kevlar felt (maximum temperature resistance 480°C), Nomex felt (maximum temperature resistance 280°C), and Polyester felt (maximum temperature resistance 180°C).
The main function of heat-resistant felt is to protect soft, high-temperature aluminum profiles from scratches and contamination, while maintaining the stability and smoothness of transport.

Working Principle—Overview
Graphite → Acts as a lubricant through its layered carbon structure
Heat-resistant felt → Protects its soft, needle-punched fiber matrix
Graphite produces carbon dust; felt does not generate any pollution
Aluminum extrusion felt can adapt to complex shapes
The properties of graphite depend entirely on its unique layered crystal structure. In this structure, carbon atoms can easily slide relative to each other, forming a natural lubricating film. This lubricating film serves the following functions:
Reduce friction when aluminum leaves the mold
Buffer heat transfer, reducing sudden temperature increases
Withstand thermal shock without cracking
Maintain structural stability during high-pressure extrusion cycles
However, during the wear and tear process of graphite, black powder and micron-sized particles will inevitably be produced. These particles easily adhere to the hot surface of aluminum, forming black marks or streaks.
This either requires additional polishing or can cause defects in the anodizing of the aluminum.
High-temperature resistant felt utilizes a flexible, dense fiber matrix that can withstand high temperatures, compression, and continuous sliding contact, providing effective protection.
Its advantages include: a soft, non-marking surface ideal for high-temperature profile processing; no graphite powder or shedding; resistance to contamination and debris embedding; uniform pressure distribution; reduced pipe scratches; and stable performance on discharge tables, cooling beds, and conveyor belts.
Resin-treated felt belt enhances abrasion resistance, enabling it to withstand continuous mechanical loads without affecting the surface quality of the aluminum profile.
Graphite plate
It has extremely high heat resistance, with a graphite melting point of 3652℃. It can work for a long time in a non-oxidizing environment below 600℃ and can fully withstand the high-temperature erosion during aluminum billet extrusion.
Heat-resistant felt
Para-aramid felt products can operate safely below 480°C, while PBO felt products can withstand temperatures up to 600°C. These temperature ranges fully meet the actual extrusion temperature requirements.
Conclusion: Graphite has higher theoretical heat resistance, but both materials can meet the temperature requirements for aluminum extrusion.
Graphite plate
Powder shedding can result in black residue, hard surfaces can cause dents or scratches on newly extruded profiles, and increase the risk of surface defects during anodizing, requiring frequent inspection and cleaning to maintain abrasion resistance and lifespan.
Heat Resistant Felt
The soft, smooth texture protects the profile surface, leaving no powder or carbon residue, and is suitable for aluminum product manufacturing with extremely high requirements for electrophoretic and polished surfaces.
PBO rollers are used at the discharge port or slide-out worktable of aluminum profile extrusion, while Kevlar rollers are only suitable for use in high-temperature areas after cutting.
Using a PBO or Kevlar roller sleeve can significantly reduce the risk of black marks and scratches, especially for high-end anodized profiles.
Conclusion: For applications with high surface finish requirements, heat-resistant felt provides far superior protection compared to graphite sheets.
Graphite plate
High hardness allows it to withstand heavy pressure, with a typical service life of 3,000–5,000 cycles, but wear increases the risk of dust, contamination, and surface damage.
Heat Resistant Felt
Heat-resistant felt, durable under mechanical loads, undergoes a resin-based hardening process to enhance its abrasion resistance and durability, significantly extending its service life.
Conclusion: Graphite performs better under extreme mechanical loads, but in most extrusion applications, high-temperature-resistant felt offers superior overall performance and fewer defects.
Graphite plate
The process generates smoke and black powder, requiring additional cleaning of profiles and production line components, leading to higher scrap and rework rates and increased labor costs for inspection.
Heat Resistant Felt
PBO felt pad/Kevlar felt pad/Nomex felt pad/polyester felt pad can replace graphite strips. Felt pads avoid the wear and blackening caused by graphite. They are especially suitable for aluminum profiles with high surface finish requirements.
According to feedback from our aluminum plant partners in Foshan, maintenance costs have been reduced by 30-40% after switching to heat-resistant felt.
Graphite Plate – Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
High temperature resistance
long service life
good stability under high pressure
Disadvantages:
Carbon powder shedding
easily scratched
requires more cleaning work
Heat-resistant Felt – Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Zero carbon dust
soft surface leaves no marks
more conducive to anodizing
Disadvantages: Shorter lifespan under extreme loads
While the initial cost of graphite sheets is generally lower, the total cost must take into account the following factors:
Surface defect rate
Scrap and rework
Labor costs for post-extrusion cleaning
Impact on anodizing or powder coating yield
Long-term profile quality and consistency. If these hidden costs are taken into account, high-temperature-resistant felt can reduce the cost per ton of finished aluminum. The following are recommended felt types based on the required temperature.
|
Temperature |
Recommended felt type |
| 180°C | Polyester felt(eg 100% polyester endless felt belt) |
|
280°C |
Nomex felt(eg 100% Nomex endless felt belt) |
|
480°C |
Kevlar felt(eg 100% kevlar endless felt belt) |
|
600°C |
PBO felt(eg, 3+7 pbo endless felt belt) |
The initial cost is lower, but as surface quality requirements increase, most modern factories have switched to heat-resistant felt to improve production efficiency.
No, if chosen properly. Resin-treated high-temperature resistant felts are specially designed for a longer service life, and their performance is generally significantly superior to untreated felts.
For complex, thin-walled, or multi-cavity aluminum profiles, heat-resistant felt significantly outperforms graphite.
For applications requiring high surface quality, contamination control, and consistent anodizing, heat-resistant felt is the superior choice. Graphite sheets are only suitable for extreme pressure areas or cost-sensitive, discreet applications.
As one of the industry’s leading high-temperature felt suppliers, we offer PBO, Kevlar, Nomex, and high-temperature conveyor belts suitable for various temperature ranges (180–600°C).
Our felts are manufactured using high-quality, high-performance fibers and advanced needle-punching processes. Our heat resistant felt products are widely used by aluminum plants in over 30 countries and are produced according to the ISO 9001:2015 quality system standard.
We work closely with extrusion plants across Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and North America, continuously improving the felt’s structure, hardness, and thermal properties based on actual production feedback.
If your plant is considering upgrading from graphite or improving surface quality and process stability, please contact us. Our engineering team can help you select the ideal heat-resistant felt solution for your extrusion production line.
This comparative analysis report was prepared by Pure Technology’s technical team, based on over 10 years of experience working with aluminum plants across Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
As we know, Heat Transfer Printing Felt is suitable for fabrics, decorative fabrics, curtains, le...
Read Safety Rules for Laundry Management to be a qualified manager. PARTⅠ Laundry room Safety Gen...
The aluminum extrusion machine is the leading equipment for the production of aluminum profiles. ...
Heat transfer printing is a contemporary printing process in the clothing market. It prints the p...
In the textile industry, felt is only a small part but important. About how to choose felt that i...
Foshan Pure Technology Company., Ltd. helps conveyor belt manufacturers source equipment to metal...
What is Nomex? Meta-amide, or meta-phenylene isophthalamide, is made from meta-phenylenediamine a...
Kevlar fiber Introduction In the development of materials science, Kevlar fiber has particularly ...