Does your ironing machine make unusual noises?
Do your operators need to constantly adjust the laundry belt’s trajectory to ensure linens are ironed in a straight line?
Does your linen wrinkle or snag easily?
If you’ve experienced any of these issues, your ironing machine’s conveyor belt may be sending early warning signals. If you’re wondering if you need to replace your ironing machine’s conveyor belt, you’ve come to the right place.
In this guide, we’ll introduce 8 key signs that your laundry belt is about to need replacing, helping you prevent linens from wrinkling and avoid costly production downtime.
Flatwork ironer belts are an essential component of your industrial iron’s functionality; because they are used in ironing machines, they are also called ironing belts.
They are generally made from high-temperature resistant materials like Nomex and polyester.
Nomex ironer belts can resist temperatures as high as 280°C, while polyester ironer belts can only resist up to 180°C. Their densities are 1200g/m² to 2200g/m², respectively.
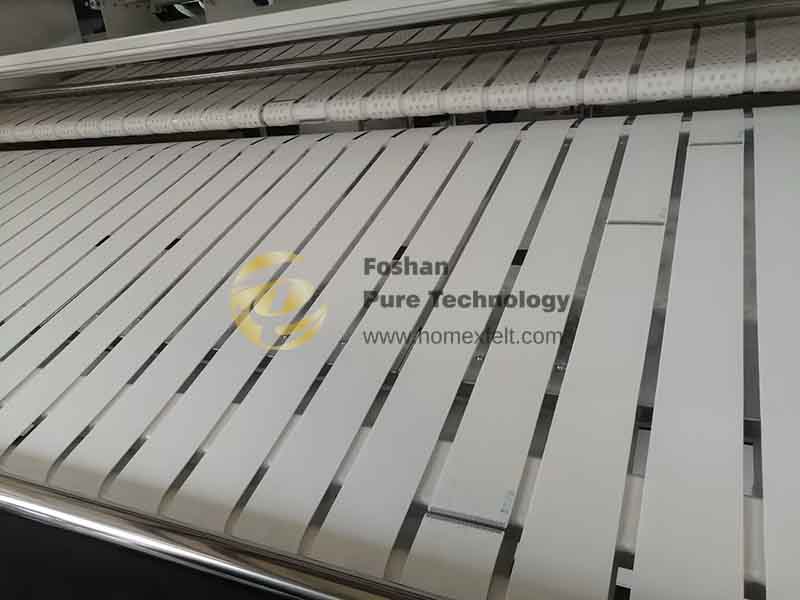

Horizontal cracks are one of the most obvious and dangerous warning signs.
During our customer visits, we found that the first ironing roller usually causes problems because it comes into contact with the dampest clothes, and chemical residues accumulate most quickly there.
When horizontal cracks appear, it is often a sign that the textile tension fibers inside the belt have begun to fail. Prolonged heat exposure accelerates thermal degradation, causing the fibers to lose strength and flexibility, eventually leading to brittleness and sudden cracking.
A case from a commercial laundry in Malaysia shows that a laundry conveyor belt with a noticeable crack malfunctioned within 48 hours, resulting in severe clothing blockage and requiring the entire machine to cool for 3 hours before the blockage could be removed.
Industry maintenance manuals from Jensen and Girbau indicate that horizontal cracks are classified as end-of-life damage because heat and moisture accelerate fiber embrittlement, leading to sudden belt failure.
Why does the ironing belt in your washing machine wear out so quickly? As laundry belts age, their surface friction decreases. Worn belts may exhibit the following appearance: roughness or unevenness; thinning in areas of high stress. Reduced friction leads to: poor ironing quality; increased wrinkles; and slower ironing machine speed.
Edge damage is typically caused by continuous contact between the fabric and the laundry belt or machine frame.
Some ironers use guide tapes (such as PPS guide tape) to help stabilize belt movement and reduce edge wear.
Signs include: loose fibers, scorch marks, and curled or deformed edges. If not addressed promptly, worn edges will eventually pull on the fabric, causing wrinkles or jamming.
If operators need to adjust the belt for misalignment more frequently than usual, such as several times a day or week, it indicates that the belt has stretched or its structure has deformed.
Frequent misalignment often indicates a loss of dimensional stability, which occurs when the belt’s internal textile structure can no longer maintain uniform tension during high-temperature operation.
Belt misalignment can lead to several problems: increased mechanical wear and uneven ironing. Additionally, laundry belt misalignment can indicate that the strength of the tension fibers inside the ironing machine belt has weakened.
According to ISO 14890 guidelines on belt elongation limits, a belt that requires frequent tracking adjustments has exceeded its structural stability threshold and should be replaced or shortened.
This is one of the last and worst signs: with an aging ironer belt, any cracks, rough surface, or loose fibers can cause linens to jam rather than flow smoothly.
Linens can become tangled inside heated rollers and cause a risk of burning, prolonged downtime, and high-temperature safety hazards. During peak seasons, shutdowns caused by jamming can last several hours.
When the flatwork ironer belt friction decreases or its thickness reduces, heat transfer efficiency decreases. This leads to the need for more steam, increased operating costs, and reduced efficiency.
As the belt surface wears down or becomes thinner, its heat transfer efficiency decreases. This forces the ironer to consume more steam to achieve the same drying and pressing performance.
According to energy-efficiency studies referenced by the European Textile Services Association (ETSA), worn ironer belts lead to measurable losses in heat transfer efficiency.
All textile-based ironer belts experience elongation under load as part of normal operation. However, once elongation exceeds the range that the tensioner can compensate, the belt can no longer deliver stable tracking or maintain dimensional stability, and replacement becomes necessary.
Textile belts naturally elongate over time. ISO 14890 and Fenner Dunlop’s belt maintenance guidelines both state that when the tensioner reaches its maximum travel, and the belt remains slack, the belt has surpassed its operational elongation range and should be replaced immediately to avoid tracking failure.
High-speed ironing machines (operating speeds exceeding 40-50 meters per minute) place higher demands on their conveyor belts.
These laundry belts must meet the following requirements: they must be made of higher-grade fibers, each ironer belt must be of a different length, they must operate under higher tension and temperature, and they must have higher dimensional accuracy. Replacement belts must be readily available if wear occurs to prevent issues such as fabric jams or sudden belt breaks that could cause downtime.
In many factories, even a minor problem with a high-speed conveyor belt can immediately halt production.
Regular maintenance can extend laundry belt life and prevent sudden failures.
Daily Inspection: Check for any cracks, wear, or scorched edges; check belt running stability; check for abnormal noise or vibration; observe ironing quality and linen production.
Weekly Inspection: Check the change in belt thickness; test the flexibility of the belt by hand; check the tension of the belt; remove chemical residues and lint.
Monthly Inspection: Compare steam consumption; record ironing speed and verify its stability; carefully inspect the first roller belt (the most worn area); record the results of each inspection to identify long-term trends.
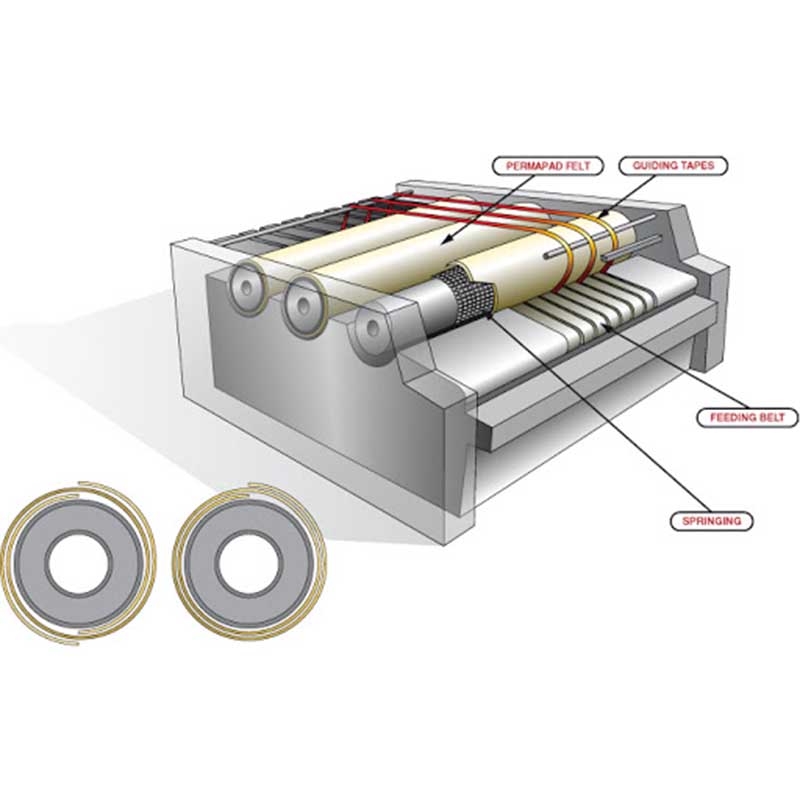
Replacing laundry belts only after a malfunction is the most expensive strategy. A better approach is predictive replacement, which involves replacing the laundry belt before it causes downtime.
Ideal replacement times include: when cracks begin to spread, when there are too many routine adjustments, before peak operating periods, when the tensioner reaches its maximum, and when ironing quality noticeably declines.
For high-speed ironing machines, numerous manufacturers suggest changing the cloth before peak seasons-for example, before Chinese New Year or before the summer hotel season-but this is because shipping delays and holiday shutdowns can cause equipment malfunctions.
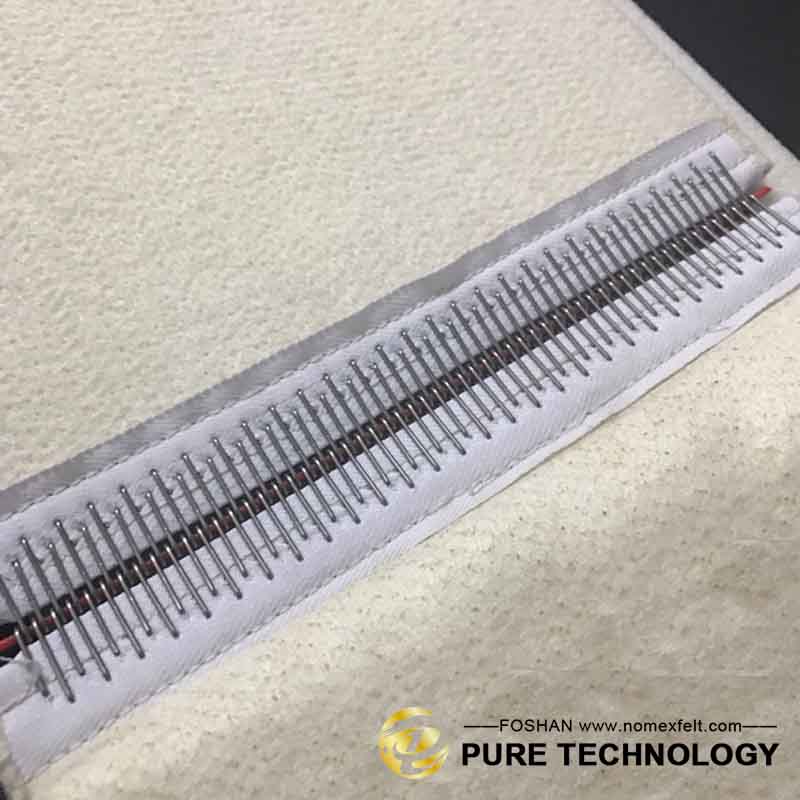

That might be due to uneven lengths in the belts, incorrect adjustment of the tensioning shaft springs, roller problems, or sometimes a bent conveyor belt shaft.
Small cracks may be usable for a short period, but horizontal cracks usually widen rapidly, so replacement is recommended.
It depends on the temperature, load, and chemical exposure. High-speed irons may need to be replaced every 6-12 months.
Yes. Reduced heat transfer efficiency forces the system to consume more steam.
High-speed ironers often require complete belt sets to maintain consistent tracking.
Pure Technology designs high-temperature ironing machine belts specifically for industrial laundry equipment. Our conveyor belts are designed to offer: longer service life and precise dimensional accuracy using high-temperature Nomex fibers and polyester fibers, suitable for both standard and high-speed ironing machines.
They provide stable operation, controllable friction for consistent ironing quality, and a reliable supply with fast shipping to Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and North America.
Our engineering team can also assist with choosing the laundry belt for your machine brand and providing customized maintenance guidance based on your production volume.
A stable ironing machine belt means less tangling of fabric, higher productivity, lower steam costs, and an overall smoother operation. Whether you want to upgrade your existing laundry conveyor belt, purchase high-temperature resistant felt for the laundry industry, or prepare for the peak season, you can contact our team is ready to help you.
As we know, Heat Transfer Printing Felt is suitable for fabrics, decorative fabrics, curtains, le...
Read Safety Rules for Laundry Management to be a qualified manager. PARTⅠ Laundry room Safety Gen...
The aluminum extrusion machine is the leading equipment for the production of aluminum profiles. ...
Heat transfer printing is a contemporary printing process in the clothing market. It prints the p...
In the textile industry, felt is only a small part but important. About how to choose felt that i...
Foshan Pure Technology Company., Ltd. helps conveyor belt manufacturers source equipment to metal...
What is Nomex? Meta-amide, or meta-phenylene isophthalamide, is made from meta-phenylenediamine a...
Kevlar fiber Introduction In the development of materials science, Kevlar fiber has particularly ...